The skills gap presents a major hurdle in the current labor market due to a mismatch between the qualifications job applicants have and what employers need. Studies show that about 25% of job requirements underwent changes from 2015 to 2024, and experts anticipate that almost half of all employee skills could become outdated by 2028. Resolving the skills gap should be a top priority. Several key factors contributing to this problem include:
- Rapid technological advancements outpace the rate at which workers can adapt or retrain.
- Educational institutions sometimes lag in aligning curricula with current industry needs.
- Changing business landscapes require new skill sets that are not yet prevalent in the workforce.
- The retirement of experienced workers leaves a void that newer entrants are not yet equipped to fill.
Understanding this problem is crucial for tailored workforce development strategies.
Identifying Skills Shortages
Determining skills gaps is a crucial component of job data analytics, which entails closely examining the present labor market to identify areas where there is higher demand than available talent for particular occupational skills. This assessment forms the basis for comprehending and guiding workforce development initiatives. It requires a comprehensive review of:
- Employment trends
- Educational output data
- Job postings
- Industry growth forecasts
When job data providers collect, analyze, and interpret relevant information, they reveal existing skill gaps that hinder economic growth. As a result, educational organizations and employers gain valuable insight necessary to customize curricula and training initiatives that develop a skilled workforce capable of adapting to the ever-changing landscape of modern industries. This targeted strategy empowers learners to acquire essential knowledge and expertise required by companies operating within the broader economy.
The Role of Job Data Providers in Closing the Skills Gap
Job data providers serve as essential partners in workforce development efforts by supplying valuable intelligence regarding present and emerging labor market dynamics. These organizations gather, evaluate, and disseminate knowledge related to:
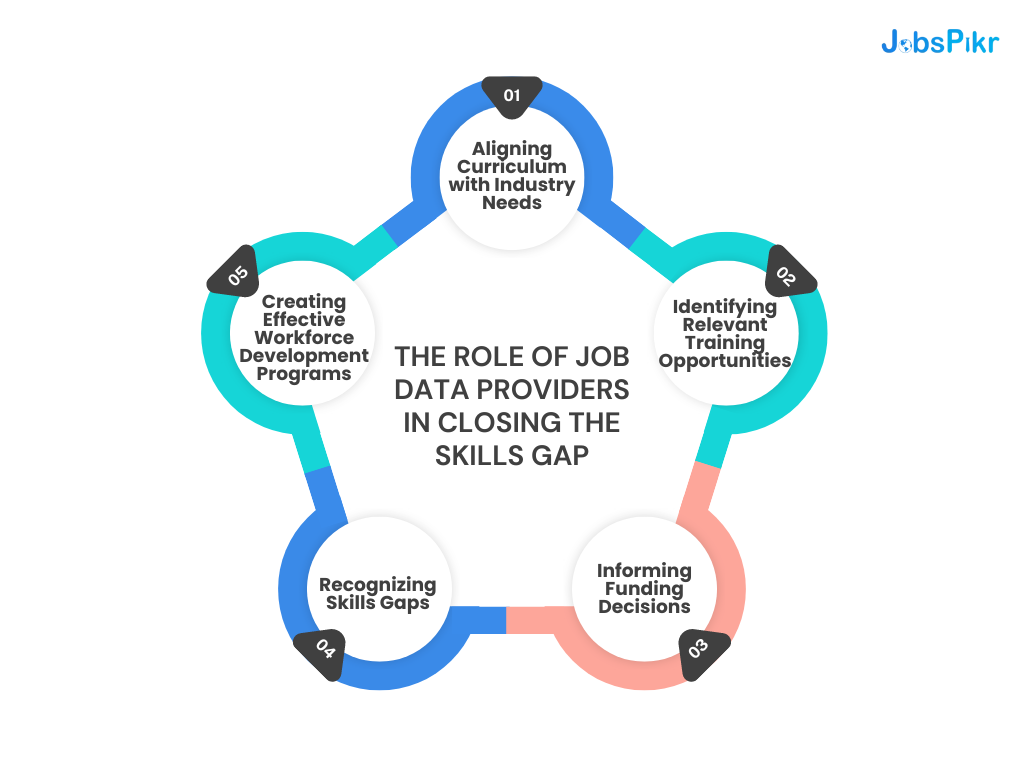
- Help educators align curricula with industry needs.
- Enable job seekers to identify and pursue relevant training.
- Inform policymakers on where to focus funding for workforce programs.
- Assist employers in recognizing and communicating skills gaps.
- Guide workforce development organizations in creating effective programs.
Through such valuable data, stakeholders are better equipped to address and close the skills gap efficiently.
Identifying In-Demand Jobs and Skills Through Labor Market Analysis
Labor market analysis is pivotal for detecting emerging opportunities and skill deficits. Job data providers dissect employment trends, highlight growing sectors, and underscore required qualifications. They cross-reference educational outputs with job market needs, spotlighting:
- Technological competencies are increasingly sought in IT and data science roles.
- Healthcare proficiencies are essential in aging populations.
- Soft skills like critical thinking and collaboration, are universally valued across industries.
Ensuring that this information is disseminated to appropriate parties like educators and policymakers allows for necessary modifications in curricula so that they align with industry requirements, consequently contributing to bridging the gap in skills.
The Interplay Between Job Data Providers and Educational Institutions
Job data providers and educational institutions engage in a critical partnership that informs curriculum design and skills development. Providers offer valuable labor market insights, revealing emerging industry trends and in-demand skills that educational institutions integrate into their programs.
This synergy ensures that curricula stay relevant and graduates possess the competencies employers seek. Partnerships may also foster targeted training initiatives, internship opportunities, and career advisory services, aligning academic outputs with the realities of the job market and effectively addressing the skills gap.
How Job Data Enhances Employee Training and Development Programs
Job data providers offer vital insights that can significantly enhance employee training and development programs. By understanding the specific skills and competencies in demand within an industry, companies can tailor their training programs more effectively to fill those needs. Here are several ways job data supports workforce development:
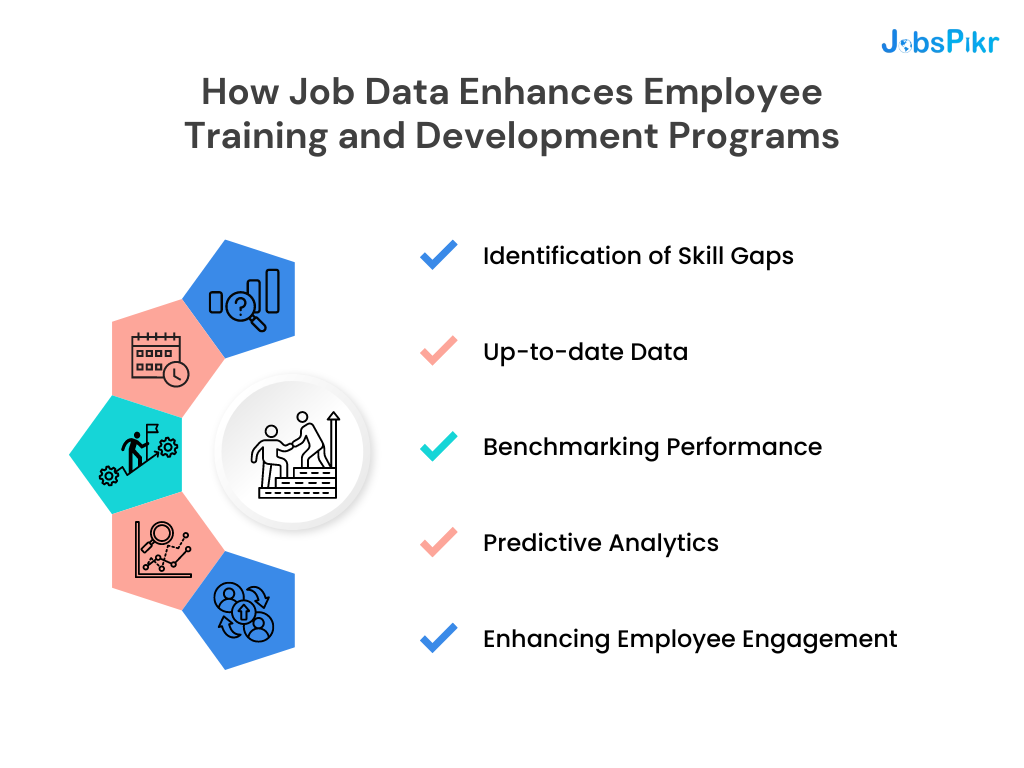
- Identification of Skill Gaps: Analyzing job data helps in pinpointing the exact skills lacking within a current workforce, allowing for targeted training initiatives.
- Up-to-date Data: Access to up-to-date job requirements ensures training materials remain relevant and aligned with market needs.
- Benchmarking Performance: Job data enables companies to benchmark their training outcomes against industry standards and competitor practices.
- Predictive Analytics: Leveraging job data through predictive analytics can forecast future skills demands, ensuring training programs are future-proofed against industry changes.
- Enhancing Employee Engagement: When employees receive training that is directly applicable to their career progression, they are more likely to be engaged and motivated.
Empowering Individuals to Make Informed Career Decisions
Providing accurate job data equips individuals with the insights needed to navigate their careers strategically. By analyzing the current demand for skills and forecasting industry trends, job data providers facilitate:
- Tailored education and training, guiding learners towards in-demand competencies.
- Career changes that align with market needs, maximizing job security.
- Personal growth plans that consider future job market directions.
Empowered by this knowledge, workers can make proactive, informed decisions to advance professionally and contribute meaningfully to the evolving workforce.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Using Job Data for Workforce Development
- Privacy Concerns: Collecting and utilizing job data must respect individual privacy. Adequate safeguards against unauthorized access to personal data are critical.
- Data Accuracy: The reliability of job data is vital. Inaccurate data can lead to misguided workforce development strategies.
- Bias and Discrimination: There’s a risk that data analytics could perpetuate existing biases in hiring practices, disadvantaging certain groups.
- Transparency: Organizations must be transparent about how job data is used, allowing individuals to understand the implications for their employment prospects.
- Access Equality: Ensuring equitable access to opportunities created by job data insights is a challenge that must be addressed.
Tracking Progress Toward Closing the Skills Gap
It’s vital to monitor progress methodically when aiming to assess success in addressing the skills gap. Suitable key performance indicators (KPIs) could be:
- Employment Rates: Monitoring job placement figures post-training to assess the impact of workforce development programs.
- Earnings Growth: Evaluating salary increases for individuals who have upskilled, indicating economic advancement.
- Skills Acquisition: Tracking certifications and degrees obtained in relevant fields, demonstrating knowledge gain.
- Employer Satisfaction: Surveying employers to determine if the skills provided match their needs, ensuring alignment between training and industry requirements.
- Job Data Accuracy: Assessing the reliability of job data provided to adjust programs accordingly for better outcomes.
Regularly reviewing these metrics ensures that strategies are effective and dynamically informs efforts to bridge the skills gap.
Conclusion
It’s crucial to develop a skilled workforce by combining job data insights. Cooperation between employers and educators is essential, using analytics to customize training that addresses current skills shortages.
By harnessing real-time job market data from job data providers, it’s possible to create curricula and courses matching industry demands, resulting in a flexible and well-prepared workforce.
This tactical approach requires ongoing adjustment for new technologies and changing job expectations, thereby strengthening and vitalizing the overall economy.




