Introduction to Global Labor Markets
Global labor markets concern the extensive arena wherein labor supply and demand meet across national boundaries. A significant element in this context is multinational corporations (MNCs), which operate in various countries, dealing with intricate regulatory systems, diverse cultures, and fluctuating economies to acquire top-tier global talents.
By formulating efficient global labor market strategies, MNCs can effectively manage their workforces, maintaining a balance of necessary abilities and assets to stay competitive. This dynamic global labor market environment is influenced by several components, including but not limited to technological progression, alterations in population distributions, and prevailing worldwide economic patterns.
To successfully integrate their human resource efforts with international corporate objectives, it is imperative that MNCs recognize and adapt to these influential elements.
Evaluating the Benefits of a Global Workforce
A global workforce offers multinational corporations (MNCs) a diverse array of advantages. Key among these are:
- Increased Market Insight: Local employees bring a nuanced understanding of their markets, helping MNCs tailor strategies to regional preferences.
- Broadened Talent Pool: By sourcing talent globally, MNCs access a wider range of skills and competencies, fostering innovation.
- Round-the-Clock Productivity: Time zone differences enable continuous business operations, improving response times and service delivery.
- Cost Optimization: Global labor markets allow for strategic relocation of certain business functions to regions with cost advantages.
- Cultural Diversity: A multicultural team can boost creativity and provide multiple perspectives in problem-solving processes.
Together, these benefits contribute to the competitiveness and success of MNCs in the global market.
Overcoming the Challenges of Cross-Border Employment
Cross-border employment management presents several difficulties for multinational corporations. It is essential that these companies familiarize themselves with and adhere to the labor regulations of every nation where they have a presence to effectively handle the legal intricacies involved. This requires robust legal frameworks and frequent consultation with local labor experts.
In terms of cultural barriers, corporations should implement diversity and inclusion programs to ensure a respectful and integrated workplace. For taxation issues, proactive planning and international tax advice are crucial to optimize tax efficiency and compliance.
Additionally, establishing clear communication channels and utilizing technology for virtual collaboration are vital for managing a geographically dispersed workforce. By addressing these challenges with informed strategies, corporations can leverage global talents and maintain competitive advantage.
Strategic Planning for International Labor Engagement
Multinational corporations must establish meticulous strategic plans to navigate global labor markets effectively. Key elements include:

Image Source: 6 Steps to Develop an Employee Engagement Plan
- Assessing geopolitical stability and labor laws in potential markets to ensure regulatory compliance and risk mitigation.
- Identifying skill shortages and surpluses globally to align workforce planning with market dynamics.
- Building robust relationships with local stakeholders, including unions and government bodies, fosters positive labor relations.
- Implementing culturally sensitive training programs that enhance skill sets and bridge cultural differences within diverse workforces.
- Leveraging technology to manage and integrate international labor resources, improving collaboration and productivity across borders.
Compliance with Legal and Ethical Standards
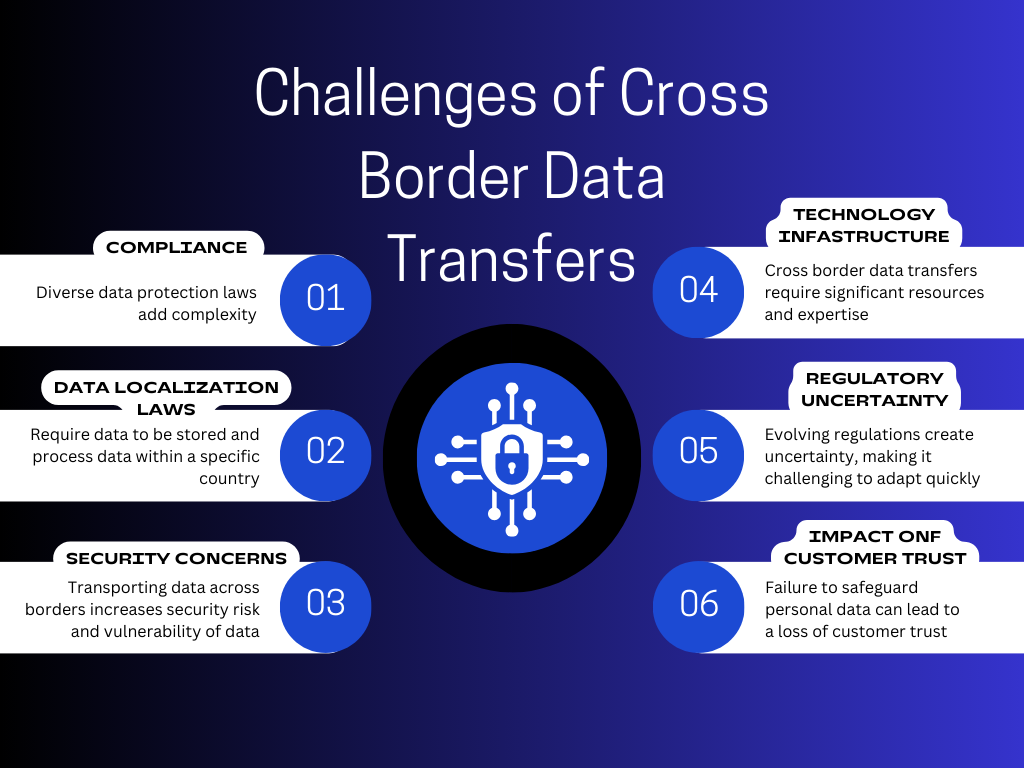
Image Source: https://dualitytech.com/blog/cross-border-data-transfer/
Multinational companies encounter the difficulty of abiding by multiple national legal systems. Compliance with globally recognized labor norms, such as those defined by the International Labour Organization, is vital for businesses to evade legal complications and sustain a desirable corporate brand. Going beyond mere compliance and adopting elevated ethical practices enables corporations to exhibit their commitment to social responsibility and establish themselves as enlightened entities within society.
Strictly implementing fair labor practices and equality policies helps multinationals gain the trust and loyalty of their worldwide employees, leading to smooth operations and lasting success. Establishing consistent corporate standards that meet the top legal and moral criteria is vital when creating global labor market strategies.
Best Practices for Managing a Multinational Workforce
- Understand cultural differences by providing intercultural training and promoting awareness.
- Implement a global human resources management system to streamline processes and maintain compliance.
- Foster communication by leveraging technology for collaboration across different time zones.
- Encourage global mobility with policies that support international transfers and assignments.
- Develop leadership that is skilled in navigating diverse cultural landscapes and managing remote teams.
- Establish a clear vision and shared corporate culture to unify employees under common goals.
- Provide equitable benefits and compensation, adjusted for local standards and cost of living.
- Ensure legal compliance by keeping up-to-date with labor laws in each country of operation.
- Invest in continuous learning and development programs to upskill the workforce globally.
- Promote employee well-being through work-life balance initiatives and mental health support.
Conclusion
Multinational corporations have the responsibility to engage with global labor markets by adhering to ethical conduct and promoting lasting progress. By maintaining labor regulations, fostering fair hiring policies, and contributing to employee training programs, businesses can generate beneficial outcomes. Effective strategies involve:
- Fostering diverse and inclusive work environments
- Prioritizing the well-being and fair treatment of workers
- Collaborating with local communities for mutually beneficial relationships
- Adhering to international labor laws and guidelines
Balancing profit motives with social responsibility leads to a robust, respected global presence.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between a Program Manager and a Product Manager in the context of multinational corporations navigating global labor markets?
A: Program managers and product managers are equally important to the success of global labor market strategies in multinational firms, although they have somewhat different duties and responsibilities:
Program Manager:
- Scope: Manages a portfolio of initiatives or projects that complement the strategic objectives of the company.
- Focus: Manages resources, schedules, and stakeholders to ensure the effective execution of several related projects, frequently spanning several locations and time zones.
- Primary Accountabilities:
- Directing interdisciplinary groups and coordinating project results with organizational goals.
- Controlling project dependencies and hazards to guarantee efficient execution.
- monitoring and reporting on development to make that projects are completed on time and on budget.
- facilitating communication to guarantee strategic alignment between project teams and upper management.
Product Manager:
- Scope: Concentrates on a single product or product line’s lifespan inside the company.
- Focus: Promotes product development, introduction, and ongoing enhancement in order to satisfy consumer demand and accomplish organizational objectives.
- Primary Accountabilities:
- Carrying out market research to comprehend consumer demands and industry developments.
- Defining the roadmap, strategy, and vision for the product in accordance with business objectives.
- Working together to develop and introduce goods with the engineering, marketing, and sales departments.
- Collecting and evaluating consumer input to direct product improvements and guarantee market fit.
In the Context of Global Labor Markets:
Program Managers might manage initiatives like global talent acquisition programs, international training and development projects, or cross-border compliance efforts. They ensure these programs are integrated, efficient, and aligned with the company’s global strategy.
Product Managers might focus on developing products that cater to diverse markets, considering local preferences, regulatory requirements, and competitive landscapes. They ensure the product meets the needs of customers in various regions and complies with local standards.
By understanding and leveraging the distinct roles of Program Managers and Product Managers, multinational corporations can better navigate the complexities of global labor markets, ensuring both strategic execution and market responsiveness.



