- **TL;DR**
- TCS Layoffs: Fast Facts & Timeline
- The Five Key Takeaways:
- India’s Layoff Wave, Contextualized
- The Hiring Paradox & GCC Revolution
- Skills revolution – What is actually in demand
- The Scale of the Skills Gap
- Shifting Boundaries of IT: A Second Tier to the Cities
- The Numbers Tell the Story
- Economic Context and Industry Analysis
- Strategic Guidance: What This Means for Employers and Professionals
- India Tech Talent Snapshot
- FAQs
**TL;DR**
The cuts at TCS in 2025 that affect over 12,000 employees are a clear telling sign that the country’s IT sector is undergoing transformation. At TCS, the automation of skill-based redeployment coupled with stricter enforcement of 35-day bench work periods convinces the firm to focus on the utilization rate and the margin pressure. This is the optimization for earning. At TCS, automation is coupled with a focus on skill-based redeployment which results in maintaining a high utilization rate. Comparatively, TCS’s rivals are not affected at all due to the rampant white-collar tech hiring across the country. This is primary due to Global Capability Centers. At the same time, the demand for highly-specialized roles encompassing AI, cloud, and cybersecurity is witnessing a massive uptick. The country’s job market is now being led by the need for advanced and high value-added tech skills in secondary towns while moving away from generic and hierarchy-bound positions. TCS’s job cuts highlights the growing trend of a combination of declining job security and opportunity and a stronger need to embrace change as well as upskilling.
Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) announced cuts of nearly 12,000 positions, corresponding to 2% of their 613,000 strong workforce, sending shockwaves far beyond the presence of TCS’s Mumbai board rooms. In the latest TCS news, the company also decided to increase the compensation of 80% of the remaining staff. In a clearer sign of a paradox, Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in India are forecasted to increase hiring by 50% in FY26. Furthermore, the foundit white-collar hiring index has increased by 32% year on year.
Is this paradoxical? No. The answer is transformation.
The Indian IT domain is experiencing the deepest realignment of talent in 20 years. This transformation is a shift from the heavy, volume-driven, generic skills, middle-management, layered, pyramid-shaped structures to a skills-based and innovation-driven strategy. This results in a mixture of contraction and expansion in other words, TCS layoffs alongside hiring surges, skill mismatches and oversaturation of skill-based pay, and the rebalancing of metros alongside the rise of tier-2 cities.
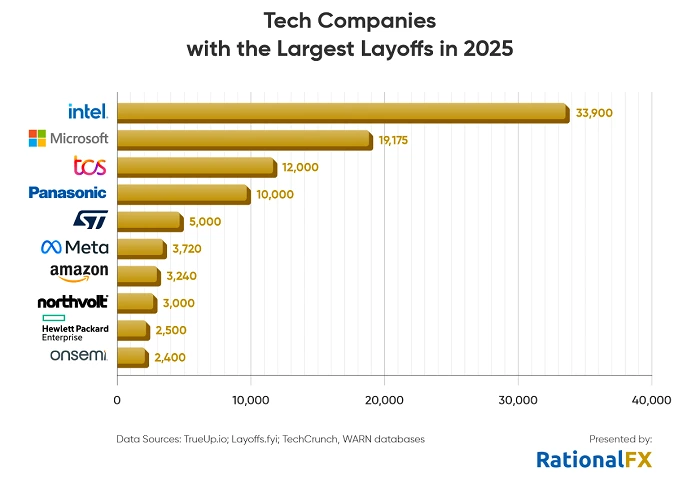
Source: electronicsmedia.info
TCS Layoffs: Fast Facts & Timeline
Key Facts, Fast Timeline, and Highlights
The story goes beyond simply TCS confirmatory headline grabbing. It showcases ever so finely extrapolated strategic shifts and maneuvers that TCS is undertaking, rather than, as many would perceive, crisis management. Here is how the framing unfolds that insinuates purposeful evolution rather than retrospective reduction:
- July 28, 2025: TCS confirms approximately 12,000 layoffs with a focus subset to predominantly mid to senior engineering and management roles. These professionals are encountering “limited deployment opportunities and skill mismatches.” Crucially, these positions are not AI automations—rather they are roles that do not compete within the company’s shifting delivery frameworks.
- July 29, 2025: After the All India Organisation of Employers claims the layoffs could potentially fall foul of current labor law, the Ministry of Electronics and IT MeitY issues a statement declaring they are “closely monitoring the situation,” MeitY Statement, highlighting the politically charged sensitivity of large scale tech layoffs in the India in the current economic situation.
- August 07, 2025: In the most telling self contradiction, TCS increases pay for about 80% of its workforce. These are C3A and below level employees, with many earning close to ₹9 lakh. This juxtaposition further bolsters the stratagem signal that the company is pursuing core competency focus.
- August 8, 2025: Union representatives are actively seeking legal interventions from the labor minister, while Karnataka’s IT minister defends the layoffs as purely strategic from a business perspective. This illustrates the multifaceted political tension related to India’s largest private sector employer’s restructuring activities.
“We are not AI-driven and looking to cut headcount. We are not doing that. We are looking at making the organization future ready.” — K. Krithivasan, TCS Chief Executive Officer.
According to industry insiders, the company’s customary 35-day bench period is now more strictly enforced. Employees who do not meet project requirements within that time frame risk being redeployed or removed to improve the overall utilization rate of the company.
The Five Key Takeaways:
- Scale: 12,000+ layoffs (2% of workforce), mostly rolling up to middle management.
- Target: Engineers and managers with non-AI-automated deployment role challenges.
- Timing: Coincides with salary raises for 80% of the existing base.
- Government Response: MeitY monitoring; legal petition from the union with no immediate action.
- Strategic Context: Transition from rigid hierarchical to fluid agile, product-centric frameworks focused on optimizing utilization rate.
This timeline depicts TCS not as a distressed company, but as a bellwether speeding up its shift to a leaner structure. This requires fewer management layers and more specialized skills.
Source: zimyo
India’s Layoff Wave, Contextualized
The TCS layoffs epitomize the most visible modifications within a much deeper, sector-wide adjustment. Technology sector layoffs within the country have now exceeded 100,000 in 2025, a number that surpasses the entirety of 2024’s total by mid-July—an astonishing acceleration that illustrates a transforming industry.
The cumulative data illustrates the increasing strain:
- January: 16,000 cuts
- February: 18,500
- March: 22,000
- April: 28,000
- May: 34,500
- June: 41,000
- July: 46,000+
There is no sifting around in an attempt to look for an explanation, this is an all-out attempt to challenge businesses in the market ecosystem. Beyond TCS, other notable contributors include Infosys with over 8,000 role eliminations, Wipro with over 5,500, and HCL Technologies reducing over 4,200 positions, along with numerous mid-tier companies implementing what they euphemistically call “performance-linked optimization” rounds.
What stands out in contrast to the rest of the 2025 timeline is how the trend is described, and how layoffs and employment res shifts, all in the redistribution of talent, rather than the reduction of workforce. For the first time in decades, the servicing sectors of IT see a constant stream of employment opportunities. A shift to new fronts centers, supported by a change in location and demand, takes over traditional IT sectors.
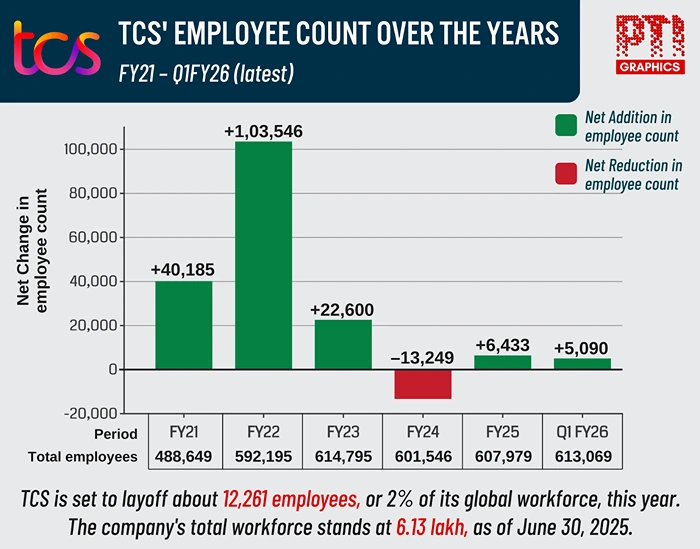
Source: Press Trust of India
The Hiring Paradox & GCC Revolution
As traditional IT services firms reduce the size of their “benches,” white-collar hiring across the country is surging to new heights. This puzzling phenomenon can be attributed to the growing presence of Global Capability Centres (GCCs).
White-Collar Hiring is Booming
Foundit’s Hiring Index rose to 347 at the beginning of 2025, marking an astonishing 32% increase year-on-year and easing margin pressure for firms able to charge higher-value rates. The current levels of the index surpass the pre-COVID benchmarks and surpass expectations despite the ongoing layoffs.
GCCs: India’s Fastest-Growing Tech Employers
GCCs have become pillars of India’s growing tech talent. Unlike the traditional service-centric approach, GCCs employ new models that pioneer innovation, R&D, and global integration.
Key Industry Metrics:
- GCCs have grown to over 1,900 in India.
- Opened 120+ new centers in 2023
- Over 2,000,000 professionals are employed.
- Forecasting 425,000–450,000 new jobs in 2025.
- 48% of GCCs expect further expansions in FY26.
Employer and Talent Appeal
Career perks: GCCs offer 15–22% higher salaries than traditional IT.
Focus on R&D: 75% of the newly opened centers since 2021, have been R&D-driven.
Accelerated Career:
- Promotions are expedited.
- Visibility into parent company strategies.
- Simpler structures and quicker hierarchies.
Technical Skill Set Benefits:
- Hands-on involvement with AI, Cloud, Cyber Security, and Gen AI.
- Cutting-edge technologies that are not available in legacy firms.
Strategic Positions:
- Considered advanced-skill-set positions and not off-shore departments.
- Focus on primary systems and do not interact with external clients.
Legacy IT vs. GCCs Net Hiring Contrast
- Old IT service firms created 11,000 new jobs in the first three quarters of FY25.
- GCCs netted over 100,000 new hires in the same timeframe.
- GCCs have outdone legacy IT firms for the second year in a row.
In summary, while the story in the news is layoffs, the reality is the narrative has shifted– from a freeze to a shift. Global innovation engines are stemming from legacy IT models alongside shifting focus from volume to value, and Global Capability Centers are spearheading this movement.

Source: ey.com
Skills revolution – What is actually in demand
There is a stark shift in the tech job market as India has seen an overemphasis on specialized capabilities, creating a need for skillsets that traditional models focused on low volume work were unable to nurture. This change is something that can certainly be measured and is happening at a rapidly innovative pace.
Top 10 technical skills that are in demand and will emerge in the future
In India, technology-related employment opportunities are increasingly shifting towards niche, high-value skills. The following skills are the most sought after.
1. AI and Machine Learning
- Annual growth in demand – 88 %
- AI-linked positions have quadrupled in comparison to older development roles.
- Leading positions – AI Researchers, Machine Learning Engineers, and Prompt Engineers
- Applicable industries – Retail, finance, healthtech, manufacturing, and nearly every industry.
2. Cloud Architecture and DevOps
- Cloud experts in India are projected to drop by 2 million professionals by FY25.
- Google Cloud, AWS and Azure are especially important since their associated skills are in greater need.
- Legendary status to certified professionals with 15-25 % salary premiums.
- Fundamental to AI and digital transformation technologies.
3. Cybersecurity
- Applicable industries – BFSI, healthtech, telecom, and government.
- High earning potential in zero trust architecture and threat intelligence.
- Increased focus due to high cyber threat levels, need for compliance, and regulatory mandates.
4. Full Stack and Platform Engineering Positions
- Increase in employment opportunities directly associated with the growth of SaaS and Fintech companies in India.
- Attention is given to the architecture and design for the system integration as well as on systems-level integration.
- Platform and API-first thinking skilled developers are in demand.
5. Data Engineering and Analytics
- Core to – AI digital twins and GenAI.
- Applicable industries – Manufacturing, healthcare, and e-commerce.
- Increased demand for data engineers with the ability to build model training infrastructure and real-time analytics pipelines.
6. Generative AI & Prompt Engineering
- GenAI is now incorporated in 1.5% of all job postings, a 2x increase compared to the previous year.
- Prompt engineers and AI content specialists are evolving as the key hybrid roles of the future.
7. Cloud Security & DevSecOps
- Increased need for specialists who can protect multi-cloud systems.
- DevSecOps roles integrating security as part of the streamlined CI/CD waterfalls.
8. Edge Computing & IoT Integration
- Most critical for smart manufacturing, automotive, and logistics.
- Need for engineers to architect distributed systems with minimal latency.
9. AI Product Management
- Integrates technology and work fluency with strategic business competencies.
- GCCs and startups are actively seeking product managers with AI/ML expertise.
10. Digital Experience & UX Engineering
- Centers on the human-AI interface, AI-assisted design, and design for all users.
- Essential for consumer applications, healthtech platforms, and the GenAI tool ecosystem.
Filling these roles is not simply a matter of possessing these attributes. They are transforming the frameworks for recruitment and skills assessment across India’s technology ecosystem. Professionals who possess hybrid skills are in greater demand, allowing them to command competitive pay in the transforming job market.
The Scale of the Skills Gap
The gap in workforce capabilities and technological adoption presents several concerning statistics:
- An estimated 2.3 million open positions in AI by the year 2027 according to Bain & Company.
- An estimated 1.2 million skilled professionals are available.
- 1.1 million gap that potentially threatens India’s digital economy aspirations.
- Generative AI makes up 1.5% of total job postings, which has doubled since last year.
The observation by LinkedIn best captures the pace of change: “50% of today’s fastest-growing roles in India did not exist 25 years ago.” The implication is straightforward. The “learn once, use forever” approach is obsolete, replaced with the need for ever-shifting skills.
NASSCOM and Deloitte’s joint survey report highlights an “AI talent crisis” which underlines the urgent need to implement aggressive reskilling programs to maintain India’s technology leadership. In a keyfinding, 48% of GCCs no longer require academic qualifications, substituting them with skill and portfolio evaluations.
Shifting Boundaries of IT: A Second Tier to the Cities
While Mumbai, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune formed the traditional IT map, that area is quickly changing. Tier 2 cities are now seeing hiring growth of 21% to 28% year on year, compared to 20% in the metros, fundamentally changing the landscape of where India’s technology talent is located.
The following new leading hubs:
- Coimbatore is also first with 26% leading driven by the merging of the City’s manufacturing industrial base with technology.
- Nagpur is also second with 24% growth, which stems from the city’s favorable central position and logistics connectivity which is a boon for regional operations.
- As an emerging technology cluster, Visakhapatnam is drawing significant attention from IT investors, especially for port-tech interfaces which integrate traditional maritime fields with contemporary digital technologies.
- Vadodara is focusing on heathcare and transportation technologies, with an emphasis on applying its industrial base as a foundation.
- Nashik shifts from being known for wine production and wineries to becoming an expanding IT and data services center.
- Jodhpur witnesses government-sponsored startup incubators with low cost-of-living, while Raipur ambitiously works on developing a semiconductor and AI hub under the ₹4.5 lakh crore Naya Raipur project.
The Numbers Tell the Story
- There is an increase in the percentage of start-up jobs in tier-2 cities from 9% to 31% year on year.
- Outside of the top six metros, 37% of all new flexible office leasing occurs.
- There is a 15-20% operational cost savings in tier-2 cities.
- Stronger talent funnels with lower attrition rates and preserved timezone alignment.
These developments are underpinned by expanded infrastructure spending. Airports and metros in smaller cities are interconnected with global centers. The PLI scheme corridors alone account for ₹1.97 lakh crore in infrastructure spending, providing over 6 million manufacturing jobs, while incorporating more tech components into manufacturing.
Economic Context and Industry Analysis
Analysts place the ongoing shift in a wider context of technological and economic drivers that go well beyond the choices of single companies. The shift marks a transformation of the global technology services ecosystem and the new places where value is created.
The assessment by NASSCOM and Deloitte in August 2024 highlights alarming issues in bold context: “Without aggressive upskilling initiatives, India risks forfeiting its AI dividend. Current talent supply trajectories will meet only half of projected demand by 2027, creating a strategic vulnerability in India’s technology leadership position.”
The shift is being captured by Gartner in May 2025: Indian IT is fundamentally pivoting from project-based armies to product-centric, agile development pods. This transformation will have a 15-20% reduction in headcount intensity while transforming productivity and innovation output per employee, a trend showcased by TCS through their layoffs paired with raises.
The Economic Backdrop:
- Revenue pressures: Relic IT service companies are experiencing a drop in revenue growth supplementary to the euro and dollar markets technology spendings, projecting a growth of only 3-4% in FY25.
- Youth unemployment: India’s urban youth unemployment is at an alarming 18.8% while the nation’s unemployment rate rests at a modest 5.6%, showcasing the K-shaped recovery curve.
- Strategic transformation consulting: Traditional outsourcing is being stifled as a result of enterprise spending, constraining the market while increasing the demand for strategic transformation consulting.
This creates a bifurcated market as a result of the mixing of the various signals: surplus capacity in generic development and maintenance skills converging with an acute scarcity in the skills of AI, cloud architecture, and cybersecurity.
Strategic Guidance: What This Means for Employers and Professionals
There are clear market signals and the TCS restructuring provides directional guidance for navigating transformation, but understanding both the opportunities and imperatives is critical for achieving success.
For Employers:
Organizational Restructuring is no longer optional. Directing cost-savings from AI-initiated upskilling and generative AI tool investments towards the pruning of mid-level management is no longer optional for businesses. Traditional pyramidal structures are yielding to cross-functional product teams which come coupled with new skill and leadership ratio requirements.
- Immediate Arbitrage Opportunities Reside in Geographic Strategy:
- Enhance tier-2 talent hubs to realize cost savings of 15-20%
- Target Coimbatore, Nagpur, Visakhapatnam
- Broaden attrition rate floors while deepening the talent pool
- Cultural and timezone proximity are preserved.
Progressive Skills-Based Hiring is becoming an imperative. 48% of GCCs who no longer require degrees have triggered a shift towards focusing on practical assessments of skills-based hiring through requisite eligibility frameworks. Reskilling investment often exceeds the ROI obtained from hiring externally. Enabling organizational loyalty while building deficient external talent skirmish scalability, investment in skill development AI/ML, cloud architecture, and cybersecurity deepens the organizational capability and loyalty.
For Technology Professionals:
Skill Prioritization becomes career defining. Focusing on advanced AI/ML certification and Cloud platform proficiency unlocks positions that come with 4x salary shifts compared to traditional development roles and provides unparalleled recession resilience compared to generic lax skills.
- Geographic Flexibility Opens New Opportunities:
- Emerging hybrid job markets
- Relocation support or telework options
- Geographically diversify career options while capitalizing on cost-of-living disparities.
Committing to Continuous Learning is essential. Research from LinkedIn shows that 70% of skills will become obsolete by 2030, which highlights the importance of proactive, routine-based, continuous learning, diffusion skill gathering for long-term career sustainability.
Adopting a Portfolio Career Approach—combining the technological fiercely specialized blended with business savvy holistic makes for starkly enhanced career competitiveness. Data scientists with product management capabilities or developers with a deep understanding of marketing for growth command premium positions with increasingly in demand roles that pure technical function specialists will struggle to reach.
India Tech Talent Snapshot
India’s technology workforce is undergoing a transformational shift, showcasing a decline in traditional roles while simultaneously adapting to more high-skill, high-demand positions. The following depicts a snapshot of some critical pointers.
- Cumulative Tech Sector Layoffs (2025): ~100,000 layoffs in 2025, surpassing 2024’s total layoffs.
- Net IT Employment Projections (2025): Growith forecast remains at 9%, with a strong hiring momentum retaining, despite layoffs.
- White-Collar Hiring Index: Index at 347 (foundit) (Up 32% y/o/y) and hitting it’s all-time peak.
- AI/ML Talent Gap (by 2027): Shortfall of 1.1 million professionals.
- GCC Footprint: 1,900+ centers operational (48% are looking to further expand in FY26).
- Hot Hiring Hubs: Coimbatore, Pune, and Hyderabad, with 20%+ job posting growth.
- Skills Premium – AI vs Traditional Roles: AI-specialized talent commanding a 4x salary differential.
- Tier-2 City Hiring Growth Rate: 21% growth y/o/y, as compared to 10% in metro cities.
India’s IT and tech industry is undergoing a significant transformation, with a shift toward specialization, regional diversification, and a skills-prioritized economy. The opportunities and risks for professionals and modern roles in demand are evolving rapidly.
The degree of transformation is illustrating an evolving threshold within which the TCS reduction of 12000 personnel sharply exemplifies. This is not an indicator of an industry crisis; it marks a strategic shift. TCS’s reduction in conventional volume positions alongside the growth of specialized innovation roles reflects mid India’s tech industry maturation.
The frontrunners are evident; those who are rapidly adopting the new skills-first distributed model and leaving behind the volume-centric approach are indisputably leading. Mark these trends until FY26. The Indian technology talent vista is in a process of rapid dynamism, offering extraordinary opportunities to those who are willing to adapt.
Note: This study, as shown in the analysis, derives its conclusions from publicly accessible information, media outlets, and other relevant sources.
Looking to get a jump on filling positions, shifts in skills thanks to retraining, or changes in available workers in a region? Look at JobsPikr for a constant stream of information on the most suitable skills, hiring trends, talent market changes, and other hiring pointers in India and other parts of the world.
FAQs
1. Why did TCS lay off 12000 employees?
Mid and senior level engineers and managers were let go in July 2025, with TCS letting go of around 12,000 employees. As the company moved towards a more agile, lean, and product-centric delivery model, these positions faced very limited skill and deployment opportunities. The organizational changes AI driven “intel” did not instigate an organizational shift.
2. Is TCS job secure?
Job security at TCS, like with most IT service companies undergoing a shift, now balances more on skill matching and readiness to be deployed. While realigned roles are at risk of a rightward shift, 80% of TCS employees saw a salary increase which shows a strong retention intent for high performing, future anticipating employees.
3. Has TCS announced a salary hike?
Indeed, TCS did increase the salary for about 80% of its employees, particularly for those in the junior, entry level and C3 positions in August 2025. This coincided with the layoff announcement, which reconfirmed TCS’s efforts to retain and reward the right talent.
4. Has TCS hiring stopped?
TCS has not made a formal statement about a hiring freeze. That said, current openings seem to be aligned with skill-based hiring, particularly in AI, cloud, and cybersecurity. While bench utilization enforcement has become stricter, targeted hiring for critical positions remains.
5. Is TCS firing employees?
Yes, TCS has started layoffs in 2025 with the cutting of approximately 12,000 employees. This is part of a greater one business strategy shift focusing on critical high-demand skills and agile delivery models in place of the traditional, staffing based, high-volume approach.




