- **TL;DR**
- What is Job Scraping?
- Turn Job Data Into Your Competitive Advantage
- How Job Scraping Works?
- Legal and Ethical Considerations in Job Scraping
- Turn Job Data Into Your Competitive Advantage
- How to Scrape Jobs from Popular Platforms?
- Best Job Scraping Tools and Services
- Turn Job Data Into Your Competitive Advantage
- Job Scraping Aggregators and APIs
- How to Scrape Jobs from Job Websites and Custom Job Platforms?
- What to Expect in the Future of Job Scraping?
- Turn Job Data Into Your Competitive Advantage
- Job Scraping vs Job Market Analytics: What’s the Difference?
- Common Challenges Teams Face & How to Solve Them (2025 Edition)
- Job Scraping in 2025: Your Blueprint for Smarter, Data-Driven Hiring
- Turn Job Data Into Your Competitive Advantage
-
FAQs
- Is job scraping legal in 2025?
- What is the difference between job scraping and job crawling?
- Can I scrape LinkedIn job postings?
- How often should job scraping be done?
- Why do DIY scrapers break so often?
- What’s the difference between scraping a job board vs. scraping company sites?
- Why use a job data provider instead of building scrapers?
**TL;DR**
Job scraping is the automated process of collecting job listings from career sites, job boards, and company pages. In 2025, it has evolved into a foundational capability for recruiters, analysts, HR tech platforms, and workforce planning teams. This job scraping guide breaks down how job scraping works, modern techniques, compliance considerations, new AI-led trends, and the future of real-time job intelligence. Whether you’re building your own scrapers, evaluating tools, or scaling hiring insights globally, this updated guide helps you make informed, compliant, data-driven decisions.
The job market in 2025 moves faster than ever. New roles appear overnight, skills rise and fall in demand within weeks, and global hiring patterns shift in real time. Relying on manual research or outdated reports can slow down recruitment, market intelligence, and workforce planning.
This is where job scraping becomes essential.
Job scraping allows teams to automatically collect structured job data: titles, locations, skills, salaries, descriptions, from thousands of sources at scale. It transforms messy, scattered information across the web into actionable insights for hiring, market research, competitive intelligence, and product development.
But job scraping today is not the same as job scraping five years ago. Tools are smarter. Legal frameworks are stricter. AI models now interpret job descriptions with deeper context. And the demand for real-time job market visibility has become non-negotiable.
This comprehensive job scraping guide brings everything together: what job scraping is, how it works, modern tools, legal considerations, use cases, 2025 trends, and how companies can safely unlock the full power of job data without burning engineering cycles or risking compliance issues.
Let’s dive in.
What is Job Scraping?
Job scraping refers to the automated collection of job listings and related information from job boards, career sites, and company websites. This data can include details such as job titles, company names, locations, salaries, descriptions, qualifications required, and more. The primary goal of job scraping is to gather large datasets quickly and efficiently, helping recruiters, researchers, and businesses stay updated with the latest job market trends.
In simple terms, job scraping is the automated process of collecting job postings and related metadata from online sources such as:
- Job boards
- Company career pages
- Niche industry sites
- Government job portals
- Recruitment platforms
- Aggregators
The scraped data typically includes:
- Industry classification
- Job title
- Company name
- Location / remote status
- Salary
- Skills required
- Employment type
- Experience level
- Job description
- Posting date / expiry
- Company metadata
How Job Data is Being Used Across Industries?
Job scraping involves using a bot or a scraping tool to “crawl” web pages to collect specific pieces of job data. This data is then used for various purposes, such as:
- Recruitment: Finding job openings that align with particular skills or roles.
- Job market analysis: Identifying trends such as salary changes, demand for specific skills, and shifts in industries hiring patterns.
- Competitive analysis: Tracking competitors’ hiring activities.
- Data aggregation: Compiling job data for research or to power job boards, search engines, or labor market reports.
Why Job Scraping Matters for Businesses and Recruiters?
Job scraping has become increasingly crucial for businesses in sectors like recruitment, HR technology, and workforce analytics. Here are some key reasons why it’s important:
- Efficiency: Manually gathering job listings is labor-intensive and time-consuming. Job scraping automates this process, freeing up valuable resources.
- Real-time Data: Scraping tools can collect fresh job postings multiple times a day, providing access to the most up-to-date information available.
- Data-Driven Insights: Job scraping provides recruiters and companies with insights into the talent market, from demand for certain skills to salary trends, enabling more informed decision-making.
- Global Reach: Job scraping allows companies to collect listings across multiple regions and industries, creating a more comprehensive view of the global job market.
Debunking Common Myths about Job Scraping
There are several misconceptions about job scraping that need to be clarified:
- “Job scraping is illegal”: Job scraping is not inherently illegal, but it can be if done without following the correct legal guidelines. As long as it complies with the terms and conditions of the sites being scraped, and does not involve collecting sensitive information, job scraping is legal.
- “Job scraping only benefits large corporations”: While large enterprises use job scraping to collect vast amounts of data, smaller businesses can benefit equally. Startups, for example, can use job scraping to keep track of industry hiring trends and stay competitive in their recruitment efforts.
- “It’s difficult to set up job scraping”: Tools and services like JobsPikr make it easier than ever to get started with job scraping without needing deep technical knowledge.
Turn Job Data Into Your Competitive Advantage
See how top HR teams and analysts use real-time job data to make smarter decisions.
How Job Scraping Works?
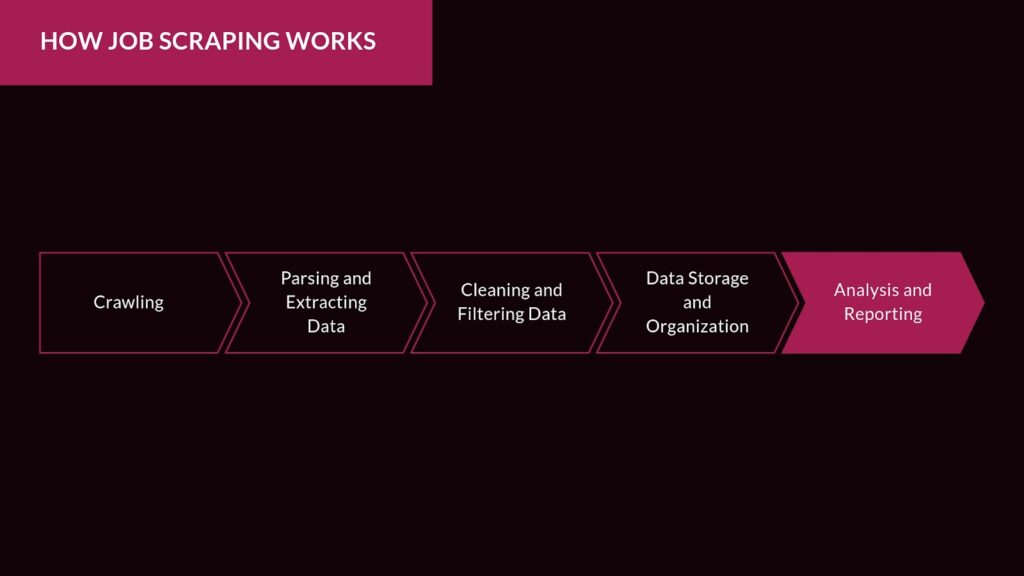
Job scraping involves breaking down the process into several distinct phases. Let’s dive deeper into the technical details:
- Crawling: Crawling is the first step in job scraping, where a bot or crawler scans the web pages for job-related content. A crawler typically follows links from one page to another, collecting information about job listings, companies, and locations as it moves through the site. This phase is crucial because it defines the scope of the scraping activity. For example, will you be scraping job boards, company career pages, or niche industry sites?
Example: A recruiter might want to scrape all job listings related to “Data Scientist” positions in “San Francisco” from multiple job boards. The crawler is set to follow links and collect job titles and details that match these criteria.
- Parsing and Extracting Data: Once the crawler identifies the relevant job pages, the next step is parsing the HTML content. This involves breaking down the raw data into structured formats. The extraction process focuses on gathering specific information such as:
- Job title
- Company name
- Location
- Job description
- Salary
- Posting date
- Application deadlines
- Advanced Parsing: Some advanced Parsing tools also extract metadata such as the job post’s unique identifier, company logo, and job category.
- Cleaning and Filtering Data: After extraction, the raw data often needs cleaning. This involves removing duplicate entries, dealing with inconsistent formats (such as different salary representations), and filtering out irrelevant or low-quality data. At this stage, companies can also prioritize or tag jobs based on certain criteria like company reputation, job relevance, or location.
- Data Storage and Organization: Cleaned and parsed data is stored in databases like SQL or NoSQL systems for easy access and analysis. Modern scraping tools often offer export options to download the data in CSV, JSON, or Excel formats, making it easier to integrate with your internal systems.
- Analysis and Reporting: Once the data is stored, businesses can perform in-depth analysis on it. This could include visualizing job trends over time, benchmarking salaries across regions, or identifying the most in-demand skills in specific industries.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Job Scraping
The legalities of job scraping depend on where, how, and what kind of data is being scraped. Websites often have terms of service (ToS) that explicitly prohibit scraping without permission. Violating these terms can lead to legal consequences, including cease-and-desist orders, account suspensions, and even lawsuits.
1. Critical Legal Aspects to Keep in Mind for Job Scraping
- Terms of Service Violations: Many websites, such as LinkedIn, Indeed, and others, have strict ToS that prohibit scraping. Companies need to check these terms before proceeding with any scraping activity.
- Data Privacy Laws: The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have strict guidelines on collecting and storing personal information. If a job scraping tool inadvertently collects personal data, it could put the company at risk of violating privacy laws.
- Court Rulings: In 2019, LinkedIn sued HiQ Labs, claiming that the company’s scraping of publicly available LinkedIn profiles violated the site’s ToS. HiQ argued that it was gathering publicly available information, and the court ruled in favor of HiQ, allowing them to continue scraping public data. However, this case underscores the need for businesses to stay informed about the evolving legal landscape around scraping.
2. Ethical Guidelines in Job Scraping
Apart from legal concerns, companies must also focus on ethical practices when scraping job data:
- Respect Website Policies: Even if the legal environment allows for scraping, companies should respect website policies and avoid aggressive scraping techniques that overload servers.
- Transparency: If scraping involves collecting personal data, businesses should be transparent about how that data will be used and ensure they obtain consent where necessary.
- Quality Over Quantity: Rather than scraping vast amounts of irrelevant data, businesses should focus on collecting high-quality, relevant data to minimize waste and avoid misleading conclusions.
3. Ethical Job Scraping: Best Practices and Guidelines
- Comply with ToS: Always check and comply with the terms of service of the websites being scraped.
- Use Data Responsibly: Avoid collecting personal data unless it’s essential and allowed by law.
- Limit Frequency of Scraping: To avoid overwhelming the source server, set limits on the number of requests made in a given period.
Turn Job Data Into Your Competitive Advantage
See how top HR teams and analysts use real-time job data to make smarter decisions.
How to Scrape Jobs from Popular Platforms?
In this section, we’ll dive deeper into job scraping for specific platforms, namely LinkedIn and Indeed, which are two of the largest and most important sources of job data for recruiters and market analysts. Both of these platforms have unique technical and legal challenges for job scraping.
1. LinkedIn Job Scraping
LinkedIn is a professional network with millions of job postings and professional profiles. Due to its wealth of structured data, LinkedIn is highly valuable for job scraping. However, scraping LinkedIn requires careful consideration due to its strict policies on data access.
Why Scrape LinkedIn for Jobs?
LinkedIn provides valuable insights that go beyond job postings:
- Professional networks: Scraping job postings along with the company details and candidate profiles gives a holistic view of the talent pool.
- Industry insights: Scraping LinkedIn helps analyze which industries are hiring, emerging roles, and specific skill sets in demand.
- Competitor Analysis: Companies can track their competitors’ hiring activities and gain insights into workforce expansion plans.
Legal and Ethical Considerations for LinkedIn Scraping
LinkedIn prohibits scraping in its Terms of Service, especially without permission. In fact, LinkedIn has taken legal action against companies like HiQ Labs for scraping public profile data. Even though HiQ Labs won the case, the issue of data scraping legality remains controversial. Companies need to:
- Check Terms of Service: Always review LinkedIn’s guidelines.
- Limit scraping frequency: High-frequency scraping activities can lead to IP bans or legal actions.
- Consider alternative data sources: To avoid legal risks, companies can supplement scraping with publicly available data from APIs and other sources.
Use Cases for LinkedIn Job Scraping
- Job Matching and Recruitment: Recruiters can scrape LinkedIn for jobs that match their candidates’ profiles and automatically generate applications or leads.
- Market Research: Firms can analyze the hiring patterns of top companies in specific industries, such as fintech or e-commerce, to predict job market trends.
- Competitor Monitoring: By tracking job openings from competitors, businesses can gather intelligence on their rivals’ expansion plans, especially in new markets.
2. Indeed Job Scraping
Indeed is one of the largest job boards in the world, hosting millions of job postings across various industries and locations. Scraping Indeed is invaluable for recruiters and businesses looking to collect large datasets of job openings for real-time analysis.
Overview of Indeed Job Scraping
Indeed’s sheer volume of job listings makes it a prime target for scraping. Some reasons businesses scrape Indeed include:
- Comprehensive Job Listings: Indeed aggregates listings from company websites and other job boards, making it a one-stop platform for collecting job data.
- Salary and Skill Insights: Companies can collect salary data to compare compensation trends and skills required for specific roles across different regions.
Challenges of Scraping Indeed
- Bot Detection Systems: Indeed uses CAPTCHA and other security measures to prevent Automated Job Scraper bots from scraping data. Bypassing these systems requires sophisticated tools.
- Rate Limiting: To avoid getting blocked, scrapers need to limit the number of requests made to the server within a given timeframe.
Best Practices for Scraping Indeed
- Use Proxies: To avoid IP blocks, companies can use proxy networks to distribute their scraping activity across multiple IP addresses.
- Avoid Scraping Too Frequently: By reducing the number of requests made per minute, scrapers can avoid detection and blocks.
- Headless Browsers: Using tools like Selenium or headless browsers that simulate human-like interaction can help bypass detection.
Use Cases for Indeed Job Scraping
- Hiring Analytics: Companies can analyze the number of open positions in specific industries, tracking where and when companies are hiring.
- Skill Gap Analysis: Scraping job descriptions allows companies to see which skills are most in-demand, helping to plan workforce training programs or hiring strategies.
- Salary Benchmarking: By scraping salary data, companies can benchmark their salary offers against industry standards, making their job offers more competitive.
Best Job Scraping Tools and Services
Here’s an expanded list of tools, categorized based on user needs (coding expertise, scale, ease of use):
Coding-Intensive Job Scraping Tools for Developers
- BeautifulSoup (Python):
- Strength: It’s highly customizable for parsing HTML and XML.
- Limitation: Requires significant coding knowledge.
- Scrapy (Python):
- Strength: Scrapy allows for scalable, large-scale job scraping projects with built-in spidering functionality.
- Limitation: Not user-friendly for non-developers.
- Selenium (Python):
- Strength: Best for scraping dynamic websites with JavaScript.
- Limitation: Slower than other scraping tools due to browser simulation.
Low-Code/No-Code Job Scraping Tools for Business Users
- Strength: No coding required; it offers a visual interface for building scraping workflows.
- Limitation: May struggle with complex websites requiring heavy JavaScript interaction.
- ParseHub:
- Strength: Good for scraping complex and dynamic websites with minimal coding.
- Limitation: It has limited features compared to custom scraping tools like Scrapy.
Advanced Job Scraping Solutions and APIs
- JobsPikr:
- Strength: It specializes in job data extraction and offers pre-configured data feeds from major job boards, including LinkedIn and Indeed. It also includes API integration for ease of use.
- Limitation: More expensive than traditional scraping tools but saves time and resources.
- WebHarvy:
- Strength: It’s a point-and-click solution for non-technical users, suitable for job scraping from basic job boards.
- Limitation: Limited for highly dynamic content and requires manual configuration for more complex tasks.
Comparing Job Scraping Services: Which One Is Right for You?
When selecting a job scraping service, businesses must consider:
- Scalability: Tools like Scrapy are best for large-scale projects that need regular data scraping. JobsPikr offers scalability without the need for extensive coding.
- Ease of Use: Tools like Octoparse and ParseHub are easier for non-technical users but may not offer the customization needed for highly specific scraping tasks.
- Cost: Third-party services like JobsPikr come at a premium but can save significant time and technical resources. Meanwhile, building a custom in-house scraping solution can have higher upfront costs but lower long-term operating costs.
Turn Job Data Into Your Competitive Advantage
See how top HR teams and analysts use real-time job data to make smarter decisions.
Job Scraping Aggregators and APIs
Job scraping aggregators compile job listings from multiple sources, such as company websites, job boards, and recruitment platforms. Rather than scraping individual websites, businesses can use aggregators to access large datasets in one place.
Popular Job Scraping Aggregators:
- JobsPikr: JobsPikr aggregates job data from multiple job boards and company websites, offering it in structured data feeds that are easy to integrate.
- Adzuna: Adzuna aggregates job data from a variety of global job boards and provides an API for accessing its data.
Benefits of Job Scraping APIs
Job scraping APIs offer an alternative to traditional scraping methods by providing structured access to job data. With APIs, businesses don’t need to scrape individual job listings manually. Instead, they can use API calls to retrieve the exact data they need.
Top Job Scraping APIs:
- JobsPikr API: Provides access to real-time job listings from multiple sources, with filters for location, industry, and job type.
- Adzuna API: Allows users to search and retrieve job listings by region, salary, and other criteria.
When to Use Aggregators and APIs
- Aggregators: Best for businesses needing comprehensive job datasets without wanting to build their own scraping infrastructure.
- APIs: Ideal for companies needing to access real-time data in specific formats or industries. APIs offer a more streamlined and legally safer option.
How to Scrape Jobs from Job Websites and Custom Job Platforms?

In addition to well-known platforms like LinkedIn and Indeed, businesses often need to scrape job data from other sources, including niche job boards, company career pages, and custom platforms. Each of these sources presents unique challenges and requires specific techniques to ensure data accuracy and legal compliance.
Challenges Involved in Scraping Various Websites
Scraping job listings from different websites is more complex than scraping from a centralized platform like LinkedIn or Indeed. Here are some challenges you might encounter:
- Website Structure Variations: Each website has a unique structure, meaning that scraping tools need to be customized for each one. A scraping script designed for a standard HTML website won’t work well on a website that uses dynamic loading with JavaScript or AJAX.
Example: Some companies have career pages that display job listings dynamically, making it difficult for traditional scrapers to capture job data without executing the site’s JavaScript.
- Bot Detection Systems: Many websites use CAPTCHA, honeypot fields, or other bot detection techniques to prevent automated scraping. Overcoming these systems often requires advanced techniques like proxy rotation, CAPTCHA solving services, and headless browsers to simulate human browsing behavior.
- Rate Limits and Bans: Most websites have a limit on the number of requests they can handle from a single IP address in a short period. If a scraper exceeds these limits, it can be banned from accessing the site. To avoid this, scrapers need to implement smart scheduling and use proxy services to spread requests across multiple IPs.
- Maintaining Data Accuracy: Job data is constantly updated as new job listings are posted, and old ones are removed. This means that scraping needs to be performed frequently to ensure the collected data is accurate and up to date. Additionally, websites might update their structure or job posting format, requiring regular updates to scraping scripts.
Why and When Custom Job Scraping Solutions Are the Right Choice?
Some businesses require custom job scraping solutions tailored to their specific needs. Custom solutions may be necessary in industries with niche job boards or specialized career platforms that aren’t covered by off-the-shelf scraping tools.
- Industry-Specific Requirements: Certain industries, such as healthcare, technology, or finance, often have their own dedicated job boards or portals. For example, a tech company might need to scrape job listings from niche boards like Stack Overflow Jobs or AngelList. In such cases, custom job scrapers built to handle the unique structures of these sites can provide more accurate data.
- Proprietary Job Platforms: Some companies host their own job boards or proprietary career platforms, which can’t be scraped using general-purpose tools. A custom-built solution allows companies to extract data without relying on third-party services.
- Complex Data Requirements: Sometimes, a simple scraping solution isn’t enough to meet specific business needs. Companies might need to scrape multiple data points, integrate them with internal systems, or perform advanced data analysis. A custom solution can be designed to handle these complex requirements efficiently.
How Custom Job Scraping Solutions Can Enhance Your Data Strategy?
- Tailored to Your Needs: Unlike general scraping tools, custom solutions are designed to meet the specific requirements of your business, whether that involves scraping niche job boards or integrating with proprietary platforms.
- Greater Control: With a custom solution, you have full control over the scraping process, ensuring that it complies with your internal policies and legal requirements.
- Scalability: Custom-built scrapers can be designed to scale with your business needs, handling increasing amounts of data as your company grows.
- Integration Capabilities: Custom scrapers can be integrated directly into your existing databases, CRMs, or applicant tracking systems (ATS), enabling a seamless flow of data between your scraper and internal systems.
Challenges of Custom Job Scraping Solutions
- Development Time and Cost: Building a custom scraping solution requires time and expertise, leading to higher upfront costs compared to using existing tools or services.
- Maintenance: As websites update their structures, a custom scraper will need to be maintained and updated regularly to ensure it continues functioning correctly.
- Legal Considerations: Just like any other scraping project, custom scrapers must comply with legal regulations, such as the terms of service of the websites being scraped and data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA.
What to Expect in the Future of Job Scraping?
As technology evolves, job scraping is poised to become even more advanced and integral to the hiring and workforce analytics industries. The future of job scraping will be shaped by innovations in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data. These advancements will significantly enhance the accuracy, speed, and scalability of job scraping activities.
Emerging Trends in Job Scraping: What’s Next?
- AI and Machine Learning Integration
One of the most exciting developments in job scraping is the increasing use of AI and machine learning. These technologies can help improve the quality and relevance of the data extracted, as well as streamline the scraping process by automating repetitive tasks. For example:
- Content Understanding: Machine learning models can be trained to better understand and categorize job listings based on the content. This allows scrapers to extract more nuanced information, such as soft skills, company culture, or job seniority levels, which might not be explicitly mentioned in the job title or description.
- Data Prediction: AI can predict future trends in the job market based on historical scraping data. For example, machine learning algorithms can analyze the job descriptions of newly posted roles to identify emerging trends in skills and job titles before they become mainstream.
- Increased Use of NLP (Natural Language Processing)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) will play a key role in improving the accuracy of job scraping. NLP can be used to analyze job descriptions in detail, helping to identify specific skill requirements, industry jargon, or even company-specific terms. This will enable more precise data collection and make the extracted job data more useful for analysis.
How AI and ML Will Transform Job Scraping?
- Faster Data Processing: AI-driven scrapers will be able to process large volumes of job data much faster than traditional methods, making it possible to analyze real-time job market trends.
- Error Reduction: Machine learning models can be trained to identify and correct errors in scraped data automatically, improving the overall quality of the dataset.
- Personalized Job Matching: AI-powered job scrapers can match job postings with potential candidates more effectively by analyzing both job descriptions and candidate profiles in detail. This will help recruiters find the best-fit candidates more quickly.
Turn Job Data Into Your Competitive Advantage
See how top HR teams and analysts use real-time job data to make smarter decisions.
How Job Scraping is Expected to Evolve in the Future?
- More Stringent Legal Frameworks
As job scraping becomes more widespread, governments and organizations are likely to introduce stricter regulations governing data collection. Laws like GDPR and CCPA already regulate how personal data is collected, and future legislation may place additional restrictions on scraping activities, especially when it comes to sensitive job market data.
- Rise of Scraping Aggregators and Services
As legal and technical barriers to scraping increase, more companies will turn to professional scraping services and aggregators like JobsPikr to meet their data needs. These services offer pre-scraped datasets and APIs, reducing the need for businesses to build and maintain their own scraping solutions.
- Real-Time Job Market Analytics
The future will likely see a growing demand for real-time job market analytics powered by scraping technologies. With the rise of remote work, changing industries, and new skill requirements, companies will rely more on real-time data to stay competitive in the hiring market.
Job Scraping vs Job Market Analytics: What’s the Difference?
| Category | Job Scraping | Job Market Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Collect raw job postings from multiple online sources. | Convert job data into insights, trends, and actionable intelligence. |
| Core Function | Automated extraction and structuring of job-related information. | Interpretation, modeling, benchmarking, and forecasting based on job data. |
| Typical Output | Cleaned datasets: titles, skills, descriptions, salaries, companies, locations. | Dashboards, reports, salary benchmarks, skill trends, hiring forecasts. |
| Required Skills | Web scraping, crawling, parsing, data engineering. | Data analysis, workforce analytics, NLP, machine learning. |
| Time Sensitivity | Focuses on real-time or near-real-time extraction. | Focuses on interpreting patterns across weeks, months, or quarters. |
| Who Uses It? | Developers, recruiters, HR tech teams, data engineers. | Analysts, workforce planners, economists, strategy leaders. |
| Value It Provides | Ensures access to accurate, fresh, structured job data at scale. | Helps companies make strategic decisions using hiring and skills insights. |
| Challenges | Breakage from site changes, legal restrictions, anti-bot measures. | Requires enriched data, taxonomies, modeling, and long-term trend visibility. |
| Dependency Relationship | Job scraping is the input. Without raw data, analytics cannot happen. | Analytics is the outcome. It relies on consistent, high-quality scraped data. |
| End Goal | Build the job data pipeline. | Derive meaning and decision-ready intelligence from the pipeline. |
Although people often use the terms interchangeably, job scraping and job market analytics serve very different functions in a modern workforce data ecosystem. Job scraping is fundamentally about collecting job postings, while job market analytics is about interpreting them to generate strategic insights.
Job scraping is an operational process. It automates the discovery and extraction of job postings from thousands of sources so organizations can build a continuously updated dataset. The focus here is on coverage, data accuracy, freshness, deduplication, and clean structuring. Scraping ensures you have the raw material—the job titles, salaries, descriptions, skills, and company details required for deeper analysis. On its own, scraping doesn’t tell you what skills are emerging or where talent shortages are intensifying—it simply gathers the underlying signals.
Job market analytics, on the other hand, is what transforms this raw information into intelligence. Analytics platforms apply classification models, skill taxonomies, enrichments, clustering algorithms, and trend analysis to reveal patterns in hiring behavior. For example, if scraped job postings show a 40% increase in AI engineering roles across Europe, analytics helps teams interpret what that means—whether it reflects a shift in technology investment, a competitive threat, or an emerging skills gap.
In 2025, the distinction between these two functions is more important than ever. Companies no longer just want job data—they want real-time workforce insights that help them make decisions around hiring strategies, market entry, compensation planning, and strategic workforce design. Job scraping is the fuel; job market analytics is the engine that converts it into acceleration.
Together, they form the backbone of modern talent intelligence solutions. But understanding where scraping ends and analytics begins helps teams build the right tech stack, allocate resources wisely, and ensure that insights—not just data—drive decision-making.
Common Challenges Teams Face & How to Solve Them (2025 Edition)
Despite its value, job scraping presents significant operational, technical, and compliance challenges. Many companies underestimate the long-term maintenance and infrastructure required to run reliable scraping at scale. Understanding these challenges—and how leading organizations solve them—helps teams avoid delays, data gaps, and costly engineering overhead.
One of the biggest issues is scraper breakage. Websites frequently change their HTML, switch frameworks, modify class names, or implement new JavaScript rendering approaches. A scraper that works today may fail tomorrow without warning. Maintaining dozens or hundreds of custom scrapers requires ongoing monitoring and engineering investment. The solution: use robust scraping frameworks with modular architecture, automated alerts, or shift to enterprise job data providers that absorb the maintenance burden entirely.
Another challenge is data overload. Companies often scrape far more job postings than they actually use, leading to massive volumes of unstructured text that consume storage, inflate processing costs, and slow analysis. The solution is to implement enrichment pipelines—skills extraction, title normalization, deduplication, salary standardization—so that data becomes insight-ready instead of overwhelming.
Compliance uncertainty is another growing concern. Teams worry about violating Terms of Service, privacy laws, or anti-bot protections. Regions like the EU and California enforce strict rules about how data can be collected and stored. Companies increasingly mitigate risk by:
- scraping only legally permitted sources
- implementing frequency caps
- avoiding personal data
- switching to compliant job data feeds such as JobsPikr’s
Finally, many organizations struggle with the engineering cost of building and maintaining scraping infrastructure. Running proxies, handling CAPTCHA, scaling servers, and managing pipeline reliability can quickly exceed expected budgets. This is why many modern teams now outsource scraping entirely and focus instead on higher-value analytics and workforce planning.
Understanding these challenges early helps organizations build more resilient, compliant, and future-proof job data ecosystems.
Job Scraping in 2025: Your Blueprint for Smarter, Data-Driven Hiring
Job scraping is a powerful tool for businesses, recruiters, and analysts looking to gain deeper insights into the job market. Whether you’re scraping job listings from platforms like LinkedIn and Indeed or building custom solutions to scrape niche websites, job scraping can provide valuable data to inform hiring strategies, market analysis, and competitive research.
As AI and machine learning continue to evolve, the future of job scraping looks even more promising. These technologies will not only enhance the speed and accuracy of scraping but will also enable businesses to extract richer, more nuanced data from job postings. However, companies must also be mindful of the legal and ethical implications of scraping and ensure they comply with data privacy regulations and website terms of service.
For companies looking to get started with job scraping, tools like JobsPikr provide a range of options, from no-code solutions to highly customizable frameworks. By carefully selecting the right tools and techniques, businesses can unlock the full potential of job scraping and stay ahead in a competitive job market.
Looking to supercharge your recruitment strategy with real-time job market data? Explore JobsPikr to learn how our advanced job scraping tools can help you collect, analyze, and act on the latest job listings from across the globe. Schedule a demo today!
Turn Job Data Into Your Competitive Advantage
See how top HR teams and analysts use real-time job data to make smarter decisions.
FAQs
Is job scraping legal in 2025?
Yes, job scraping is legal when done responsibly, respecting website ToS, avoiding personal data, and complying with privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA. Many companies now opt for compliant job data providers to eliminate legal risk.
What is the difference between job scraping and job crawling?
– Crawling finds and navigates pages.
– Scraping extracts structured data from them.
Both processes work together to build job datasets.
Can I scrape LinkedIn job postings?
Direct scraping of LinkedIn violates its ToS and carries legal risk. Most companies now rely on job data aggregators or scrape public company career pages instead.
How often should job scraping be done?
High-volume job markets require hourly or daily scraping to keep data fresh. Market analysts often refresh datasets weekly, while job boards update multiple times per day.
Why do DIY scrapers break so often?
Websites frequently change their HTML structure, add bot protections, or modify job detail pages. These changes break scraper logic unless updated manually. This is why many teams choose ready-made job data feeds.
What’s the difference between scraping a job board vs. scraping company sites?
Job boards provide aggregated job listings but have stricter anti-bot measures. Company sites often have richer metadata but inconsistent formats. Most organizations scrape both (or use aggregated job feeds).
Why use a job data provider instead of building scrapers?
Providers like JobsPikr reduce:
– Engineering effort
– Compliance risk
– Data cleaning workload
– Time-to-insight
They deliver ready-to-use enriched data, saving months of internal development.




